Early Molecular Diagnosis of Cancer Proven More Cost-Effective Than Subsequent Treatment of Advanced Disease
Applying expensive diagnostic methods in clinical practice will ultimately cost society 5 to 10 times less than the expenditures associated with late-stage cancer treatment, including subsequent disability pensions and sick leave payments—these are the findings from a study conducted by researchers at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences Marina Kolosnitsyna and Anastasia Vladimirskaya in collaboration with colleagues at EVOGEN, a medical genetic laboratory, and the Department of Health of the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug. The study results have been published in Social Aspects of Population Health.

Economists Suggest Using Media's Attention to Bitcoin to Predict its Returns
Researchers at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences have studied the relationship between the changes in the bitcoin prices and the media attention to this cryptocurrency. The researchers examined the mentions of bitcoin in the media between 2017 and 2021 and built a mathematical model that revealed the strong relationship between media attention and bitcoin prices. The study was published in the Applied Stochastic Models in Business and Industry journal.
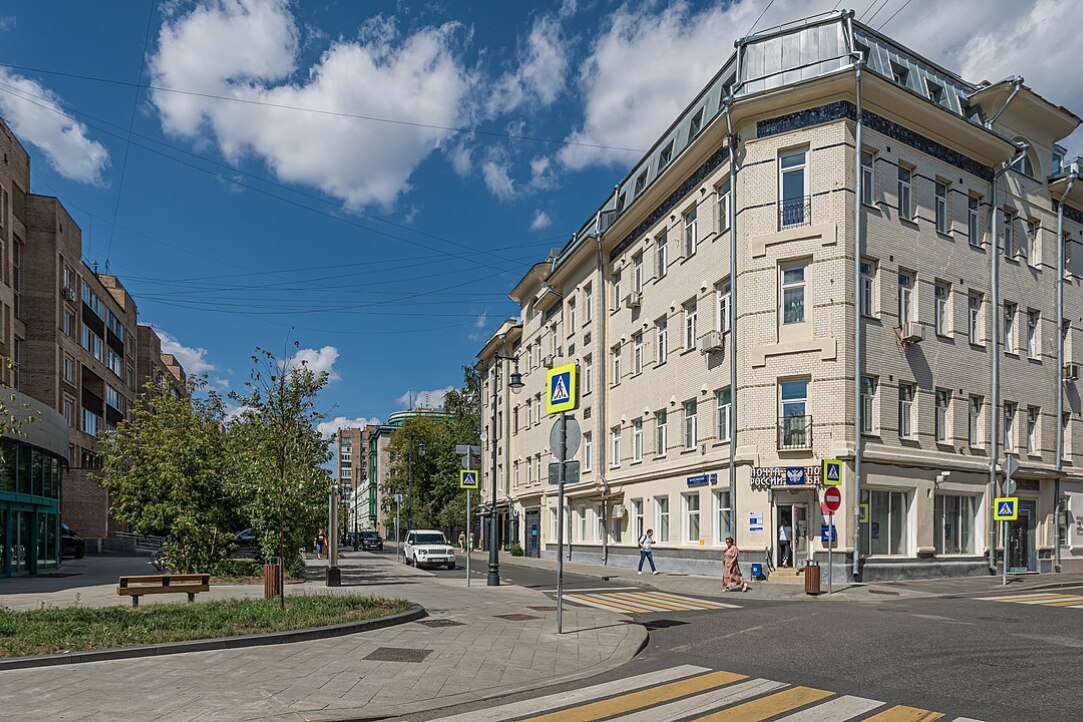

Researchers at HSE University Identify the Most Walkable Areas in Moscow
Experts at HSE University and Lomonosov Moscow State University examined the available data on Moscow's walkability and found the central and south-western parts of the city to be more walkable than others. However, the eastern and south-eastern areas are in need of improvements to make them more pedestrian-friendly. The study has been published in Cities.

Lavsan and Kapton Tested Under Space-like Radiation Conditions
In a ground-breaking experiment, HSE MIEM researchers subjected Lavsan (polyethylene terepfthalate, polyester) and Kapton (polypiromellitimide, polyimide) polymers, commonly used in space technology, to ionising radiation for durations ranging from microseconds to several hours at temperatures of -170°C and +20°C, while comparing their electrical conductivity under extreme conditions. The study reveals that at -170°C, Kapton's conductivity is ten times lower than at +20°C. These findings can assist engineers in developing more effective protection for spacecraft against static discharges induced by ionising radiation. The study has been published in Journal of Applied Physics.
Paper by HSE Biologists Included in the Top 5 Popular Articles of PeerJ Journal
An article by researchers from HSE University’s Faculty of Biology and Biotechnology is among the most read articles published in the PeerJ journal in 2023. In the paper, the researchers establish a link between the genetic characteristics of the human immune system and its ability to effectively resist new waves of COVID-19. PeerJ is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal covering research in the field of biological and medical sciences. Every year the editors compile a ranking of the most popular scientific papers.

HSE Accepting Applications for Competition of Best Russian-language Scientific and Popular Science Papers
Applications for the fourth HSE University Competition of the Best Russian-language Scientific and Popular Science Papers will be accepted from February 1 to March 15. The authors that receive the highest scores from the expert jury will be awarded on June 6—Russian Language Day. The main goal of the competition is to support and promote Russian language as a language of science, as well as to popularise works affiliated with HSE University among the global Russian-speaking audience.

HSE Economists Develop a Model for Sustainable Solar Geoengineering Agreements
Researchers at HSE University and George Mason University have investigated the sustainability of prospective international agreements on solar geoengineering. The authors have proposed a scheme in which payments flow from affluent nations to less wealthy ones; an arrangement which sets their proposal apart from traditional systems. The proposed model aims to dissuade more vulnerable countries from excessive use of the prevalent geoengineering method by providing compensation for the potential damage they may incur and supporting their adaptation to climate change. The paper has been published in Environmental and Resource Economics.

Human Bodies Impede 6G Signal Transmission
A team of researchers, including scientists from HSE University, have investigated the influence of human movement on the propagation of 6G signals. Within a range of up to 10 metres, the signal attenuation is comparatively minor, yet brief connection failures may still occur. Based on the study findings, a blockage detection algorithm has been developed to account for both signal attenuation and interruptions. The gaming industry is likely to derive the greatest benefits from this discovery. A paper with the study findings has been published in Computer Communications.

Neural Networks of Power: AI Unravels Knots and Tangles in Relationships between Humans, Elves and Hobbits
One of the most popular writers of the last century, John Ronald Reuel Tolkien, was born on January 3rd. Researchers from HSE University, AIRI and MISSIS have used machine learning to explore the social connections between the characters of his Middle-earth universe. The algorithm managed to create an accurate picture of the social structures and dynamics of the characters' relationships, providing a unique map of interactions in the epic world. The results of the work were published in IEEE Xplore.

Scientists Discover Cause of Metastasis Formation in Patients with Colorectal Cancer
An international team of researchers including scientists at the HSE Faculty of Biology and Biotechnology has identified factors which can increase the aggressiveness of tumours in patients with colorectal cancer. An isoform of CD44 protein has been found to play a pivotal role in the development of metastases. The study findings have been published in Molecular Oncology.