Electrical Brain Stimulation Helps Memorise New Words
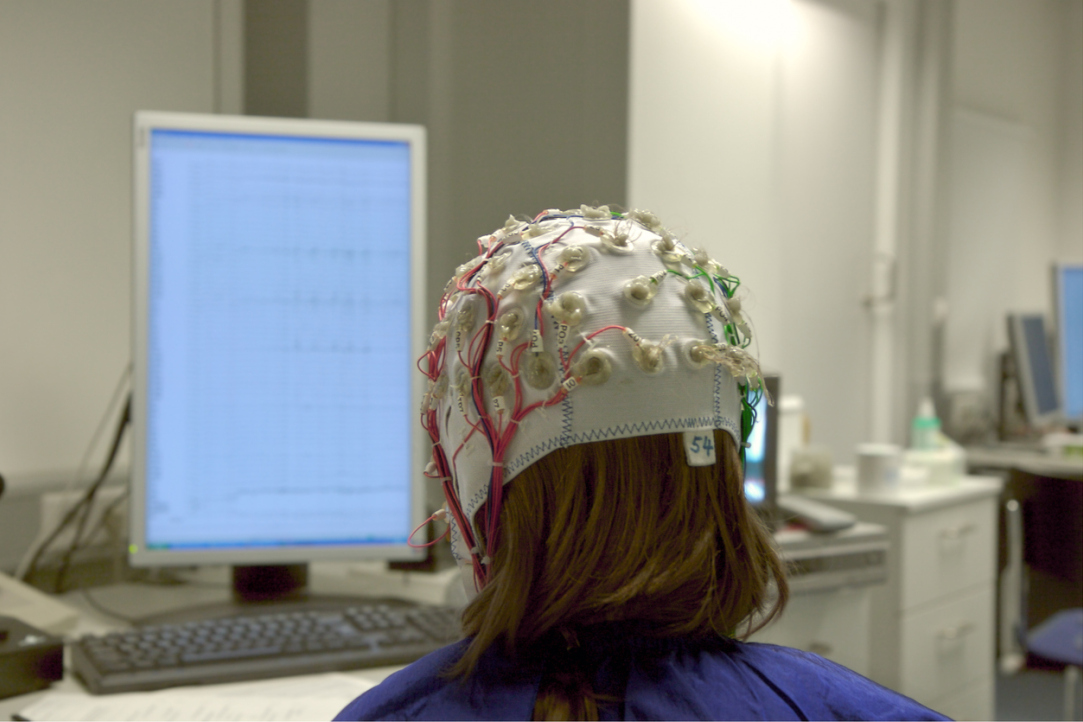
A team of researchers at HSE University, in collaboration with scientists from Russian and foreign universities, has investigated the impact of electrical brain stimulation on learning new words. The experiment shows that direct current stimulation of language centres—Broca's and Wernicke's areas—can improve and speed up the memorisation of new words. The findings have been published in Neurobiology of Learning and Memory.
The transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) technique involves applying a low direct current to specific areas of the brain. The advantages of tDCS include its simplicity, affordability, and non-invasive nature, meaning it does not require surgical intervention or expensive equipment. All that is required is the correct placement of electrodes on the head.
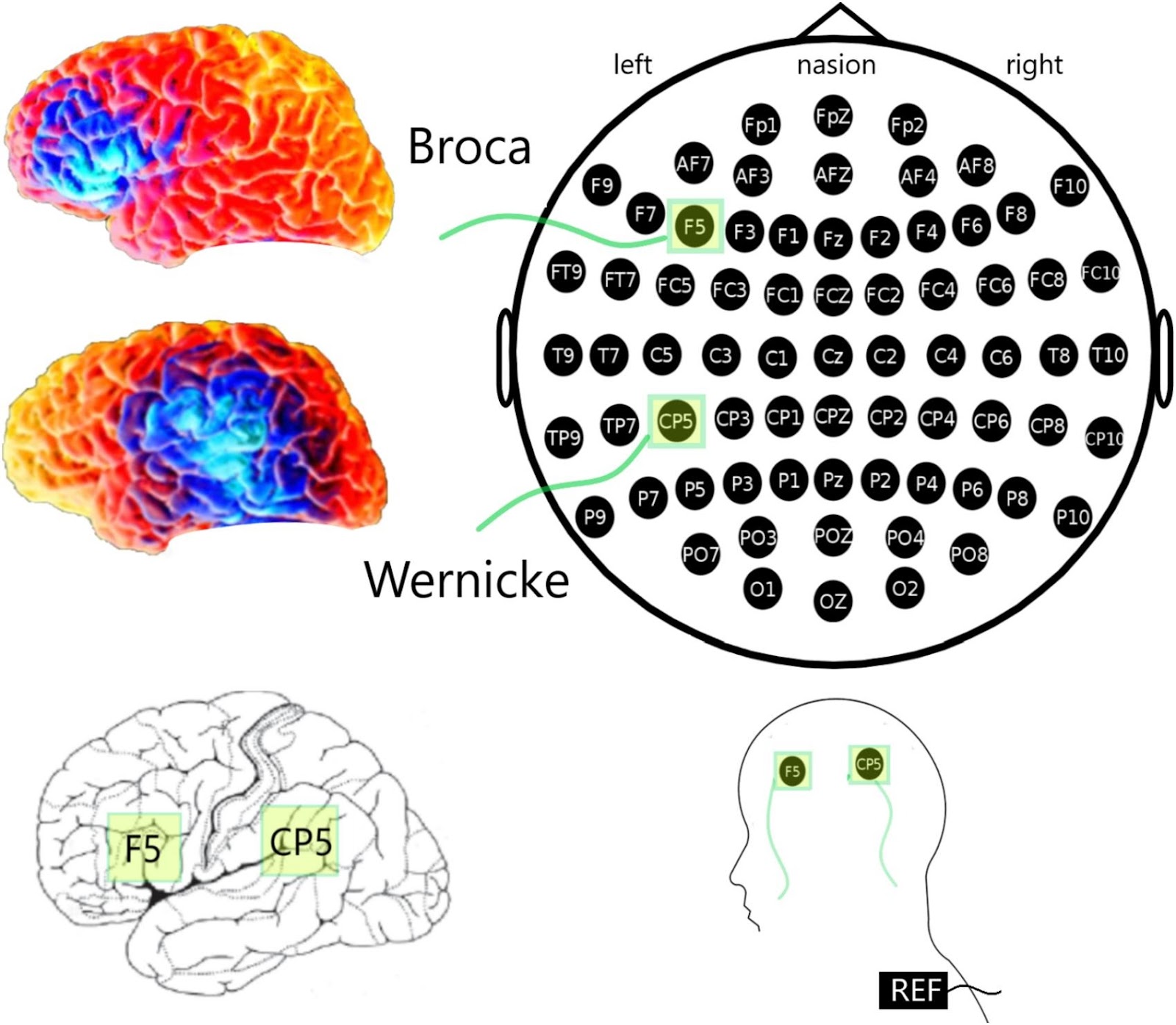
Researchers from HSE University, the N.P. Bekhtereva Institute of the Human Brain of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Sirius University, and the Gestalt Centre London, in collaboration with St Petersburg State University, investigated how transcranial direct current stimulation of Broca's and Wernicke's areas affects new word acquisition. These two areas are the brain's primary language centres, typically located in the left hemisphere for most people. The authors of the study conducted a large-scale, complex experiment involving 160 participants.

'We developed a rather complex experimental design, aiming to account for as many factors influencing learning as possible to obtain the most comprehensive picture of the process of acquiring new words. We aimed to determine whether transcranial direct current stimulation actually aids in memorising new words, whether a specific stimulation mode influences memorisation, and which brain area—Broca's or Wernicke's—plays a more significant role in the process of learning new words,' explains Olga Sherbakova, Leading Research Fellow at the Cognitive Health and Intelligence Centre of the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience.
To account for all these factors, participants were randomly assigned to five groups, subjected, respectively, to anodal stimulation of Broca’s area, anodal stimulation of Wernicke’s area, cathodal stimulation of Broca’s area, cathodal stimulation of Wernicke’s area, and placebo stimulation as a control, with inactive electrodes placed on the scalp.
The stimulation lasted 15 minutes, after which participants were instructed to memorise 16 new words—or more precisely, pseudowords—designed specifically for the experiment using the phonetic and rhythmic structure of the Russian language.
'People use two strategies to learn new words: explicit learning, where we are shown an object and told, "this is a table," and implicit learning, where we infer the meaning of a word from its context. In our experiment, we aimed to determine which memorisation strategy would be more effective under stimulation,' Shcherbakova explains. 'Additionally, we asked the participants to repeat some words aloud to investigate whether, as is commonly believed, articulation—pronouncing memorised words aloud—actually aids in memorisation.'
During the experiment, participants were shown images of unfamiliar objects, such as ancient musical instruments or rare deep-sea fish. While viewing each image, participants either heard a new word, such as 'This is SEN' (explicit strategy), or a question, such as 'Is SEN furry?' (implicit strategy).
After the learning phase, each group was assessed to determine which of them learned the new words most effectively and whether the learning strategy had any impact on the outcome. Participants first had to recognise a word by ear and then associate it with the image. The outcome assessment considered both the speed and accuracy of the response.
The results of the experiment show that both the explicit and implicit strategies lead to similarly successful word acquisition but engage different neural mechanisms, as evidenced by the varying effects of the different stimulation modes. It was also found that articulation contributes to better memorisation: participants recognised the words they had said aloud during the learning phase more accurately and quickly.
Most importantly, the study authors demonstrated that transcranial direct current stimulation significantly improves word memorisation, with the greatest effect resulting from anodal stimulation of Broca's area and cathodal stimulation of Wernicke's area. It is also important to note that the study found no adverse effects of tDCS on the outcomes of word learning in any of the groups.
This is the first tDCS study to consider such a wide range of factors potentially affecting language learning and to yield reliable results. 'We were able not only to demonstrate that tDCS has a positive effect on language learning, but also to identify the optimal stimulation modes for such learning,' Sherbakova emphasises.
In the future, the researchers plan to investigate the delayed effects of tDCS and determine how long its positive impact on the brain's language areas lasts. Potentially, transcranial direct current stimulation could be used to restore language abilities in patients after a stroke, brain injury, or neurodegenerative disease, as well as to enhance the cognitive abilities of healthy individuals.
See also:
Scientists Test Asymmetry Between Matter and Antimatter
An international team, including scientists from HSE University, has collected and analysed data from dozens of experiments on charm mixing—the process in which an unstable charm meson oscillates between its particle and antiparticle states. These oscillations were observed only four times per thousand decays, fully consistent with the predictions of the Standard Model. This indicates that no signs of new physics have yet been detected in these processes, and if unknown particles do exist, they are likely too heavy to be observed with current equipment. The paper has been published in Physical Review D.
HSE Scientists Reveal What Drives Public Trust in Science
Researchers at HSE ISSEK have analysed the level of trust in scientific knowledge in Russian society and the factors shaping attitudes and perceptions. It was found that trust in science depends more on everyday experience, social expectations, and the perceived promises of science than on objective knowledge. The article has been published in Universe of Russia.
Scientists Uncover Why Consumers Are Reluctant to Pay for Sugar-Free Products
Researchers at the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience have investigated how 'sugar-free' labelling affects consumers’ willingness to pay for such products. It was found that the label has little impact on the products’ appeal due to a trade-off between sweetness and healthiness: on the one hand, the label can deter consumers by implying an inferior taste, while on the other, it signals potential health benefits. The study findings have been published in Frontiers in Nutrition.
HSE Psycholinguists Launch Digital Tool to Spot Dyslexia in Children
Specialists from HSE University's Centre for Language and Brain have introduced LexiMetr, a new digital tool for diagnosing dyslexia in primary school students. This is the first standardised application in Russia that enables fast and reliable assessment of children’s reading skills to identify dyslexia or the risk of developing it. The application is available on the RuStore platform and runs on Android tablets.
Physicists Propose New Mechanism to Enhance Superconductivity with 'Quantum Glue'
A team of researchers, including scientists from HSE MIEM, has demonstrated that defects in a material can enhance, rather than hinder, superconductivity. This occurs through interaction between defective and cleaner regions, which creates a 'quantum glue'—a uniform component that binds distinct superconducting regions into a single network. Calculations confirm that this mechanism could aid in developing superconductors that operate at higher temperatures. The study has been published in Communications Physics.
Neural Network Trained to Predict Crises in Russian Stock Market
Economists from HSE University have developed a neural network model that can predict the onset of a short-term stock market crisis with over 83% accuracy, one day in advance. The model performs well even on complex, imbalanced data and incorporates not only economic indicators but also investor sentiment. The paper by Tamara Teplova, Maksim Fayzulin, and Aleksei Kurkin from the Centre for Financial Research and Data Analytics at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences has been published in Socio-Economic Planning Sciences.
Larger Groups of Students Use AI More Effectively in Learning
Researchers at the Institute of Education and the Faculty of Economic Sciences at HSE University have studied what factors determine the success of student group projects when they are completed with the help of artificial intelligence (AI). Their findings suggest that, in addition to the knowledge level of the team members, the size of the group also plays a significant role—the larger it is, the more efficient the process becomes. The study was published in Innovations in Education and Teaching International.
New Models for Studying Diseases: From Petri Dishes to Organs-on-a-Chip
Biologists from HSE University, in collaboration with researchers from the Kulakov National Medical Research Centre for Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Perinatology, have used advanced microfluidic technologies to study preeclampsia—one of the most dangerous pregnancy complications, posing serious risks to the life and health of both mother and child. In a paper published in BioChip Journal, the researchers review modern cellular models—including advanced placenta-on-a-chip technologies—that offer deeper insights into the mechanisms of the disorder and support the development of effective treatments.
Using Two Cryptocurrencies Enhances Volatility Forecasting
Researchers from the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences have found that Bitcoin price volatility can be effectively predicted using Ethereum, the second-most popular cryptocurrency. Incorporating Ethereum into a predictive model reduces the forecast error to 23%, outperforming neural networks and other complex algorithms. The article has been published in Applied Econometrics.
Administrative Staff Are Crucial to University Efficiency—But Only in Teaching-Oriented Institutions
An international team of researchers, including scholars from HSE University, has analysed how the number of non-academic staff affects a university’s performance. The study found that the outcome depends on the institution’s profile: in research universities, the share of administrative and support staff has no effect on efficiency, whereas in teaching-oriented universities, there is a positive correlation. The findings have been published in Applied Economics.