Habits Stem from Childhood: School Years Found to Shape Leisure Preferences in Adulthood
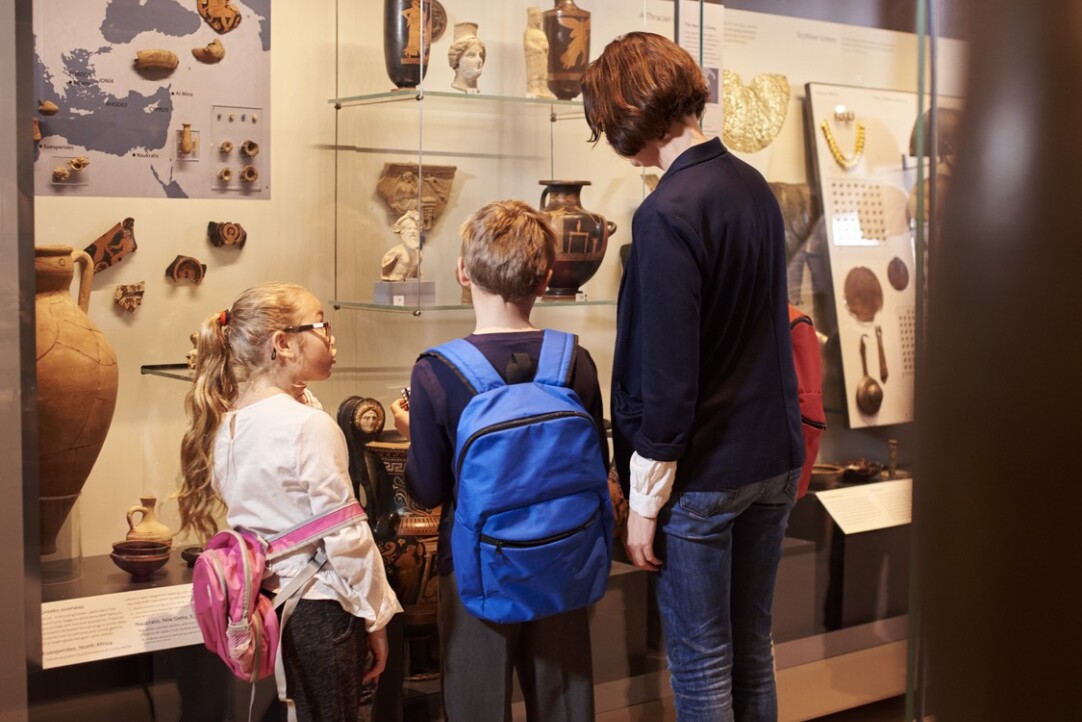

Moving to a big city does not necessarily lead to dramatic changes in daily habits. A study conducted at HSE University found that leisure preferences in adulthood are largely shaped during childhood and are influenced by where individuals spent their school years. This conclusion was drawn by Sergey Korotaev, Research Fellow at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences, from analysing the leisure habits of more than 5,000 Russians.
The environment in which a person lives shapes their daily habits, including how they spend their leisure time and the cultural and social activities they choose to engage in. However, as Sergey Korotaev, Research Fellow at the Laboratory for Comparative Analysis of Post-Socialist Development of the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences, found in a recent study, a person’s lifestyle is influenced not only by their current place of residence. The community where they spent their childhood and completed their schooling also plays a significant role.
The study is based on a dataset from the survey Social Distinctions in Modern Russia and includes over 5,000 respondents aged 24 to 55. The survey questionnaire covered a range of activities, including attending theatres, exhibitions, or sports events; drinking alcohol socially; reading books in libraries; and playing computer games. This approach made it possible to capture a broader range of everyday behavioural patterns.
The results were then mapped along three axes: active versus passive behaviour, cultured versus mundane practices, and real-world versus virtual activities. Based on this data, four behavioural clusters were identified, ranging from individuals with minimal engagement in leisure activities to those who actively participate in cultural events. The analysis revealed that higher income, education, and professional qualifications are linked to more active and cultured lifestyles. The family also plays a significant role in shaping leisure choices in various ways; for instance, parents' higher education increases the likelihood of engaging in cultured and active leisure, both in megacities and small towns.
However, it’s not only social status that influences behavioural style. The researchers examined how leisure patterns change among individuals who move from one type of settlement to another. It was found that more than a third of established habits can be attributed to where a person lived during their school years. Individuals raised in megacities are typically four times more likely to attend cultural events than those who grew up in small towns or villages.

Sergey Korotaev
'One might assume that the act of moving itself influences leisure preferences. For example, those who have relocated to a large city are likely to appreciate new opportunities more, leading to even more diverse and intense leisure activities. However, the study showed that this is not the case: the habits of those who have moved to large cities tend to fall somewhere between the habits of their hometown community and those of their new residence,' comments Sergey Korotaev, Research Fellow of the Faculty of Economic Sciences.
'The context of the move is important: whether it was driven by the pursuit of education in youth or by the need to find employment later in adulthood. This can significantly influence the imprint that a person’s spatial trajectory leaves on them. However, to fully account for this, a more complex model and additional data are needed,' according to Korotaev.
These findings raise important considerations for regional policy and urban development. Understanding how leisure habits are formed can contribute to more effective development of cultural infrastructure and provide people of different ages and living in diverse locations with the most suitable leisure options for them. The researcher emphasises that to influence people's daily activities, it is essential to consider not only their current environment but also their biographical context.
See also:
HSE Psycholinguists Launch Digital Tool to Spot Dyslexia in Children
Specialists from HSE University's Centre for Language and Brain have introduced LexiMetr, a new digital tool for diagnosing dyslexia in primary school students. This is the first standardised application in Russia that enables fast and reliable assessment of children’s reading skills to identify dyslexia or the risk of developing it. The application is available on the RuStore platform and runs on Android tablets.
Physicists Propose New Mechanism to Enhance Superconductivity with 'Quantum Glue'
A team of researchers, including scientists from HSE MIEM, has demonstrated that defects in a material can enhance, rather than hinder, superconductivity. This occurs through interaction between defective and cleaner regions, which creates a 'quantum glue'—a uniform component that binds distinct superconducting regions into a single network. Calculations confirm that this mechanism could aid in developing superconductors that operate at higher temperatures. The study has been published in Communications Physics.
Neural Network Trained to Predict Crises in Russian Stock Market
Economists from HSE University have developed a neural network model that can predict the onset of a short-term stock market crisis with over 83% accuracy, one day in advance. The model performs well even on complex, imbalanced data and incorporates not only economic indicators but also investor sentiment. The paper by Tamara Teplova, Maksim Fayzulin, and Aleksei Kurkin from the Centre for Financial Research and Data Analytics at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences has been published in Socio-Economic Planning Sciences.
Larger Groups of Students Use AI More Effectively in Learning
Researchers at the Institute of Education and the Faculty of Economic Sciences at HSE University have studied what factors determine the success of student group projects when they are completed with the help of artificial intelligence (AI). Their findings suggest that, in addition to the knowledge level of the team members, the size of the group also plays a significant role—the larger it is, the more efficient the process becomes. The study was published in Innovations in Education and Teaching International.
New Models for Studying Diseases: From Petri Dishes to Organs-on-a-Chip
Biologists from HSE University, in collaboration with researchers from the Kulakov National Medical Research Centre for Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Perinatology, have used advanced microfluidic technologies to study preeclampsia—one of the most dangerous pregnancy complications, posing serious risks to the life and health of both mother and child. In a paper published in BioChip Journal, the researchers review modern cellular models—including advanced placenta-on-a-chip technologies—that offer deeper insights into the mechanisms of the disorder and support the development of effective treatments.
Using Two Cryptocurrencies Enhances Volatility Forecasting
Researchers from the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences have found that Bitcoin price volatility can be effectively predicted using Ethereum, the second-most popular cryptocurrency. Incorporating Ethereum into a predictive model reduces the forecast error to 23%, outperforming neural networks and other complex algorithms. The article has been published in Applied Econometrics.
Administrative Staff Are Crucial to University Efficiency—But Only in Teaching-Oriented Institutions
An international team of researchers, including scholars from HSE University, has analysed how the number of non-academic staff affects a university’s performance. The study found that the outcome depends on the institution’s profile: in research universities, the share of administrative and support staff has no effect on efficiency, whereas in teaching-oriented universities, there is a positive correlation. The findings have been published in Applied Economics.
Physicists at HSE University Reveal How Vortices Behave in Two-Dimensional Turbulence
Researchers from the Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences and the HSE University's Faculty of Physics have discovered how external forces affect the behaviour of turbulent flows. The scientists showed that even a small external torque can stabilise the system and extend the lifetime of large vortices. These findings may improve the accuracy of models of atmospheric and oceanic circulation. The paper has been published in Physics of Fluids.
Solvent Instead of Toxic Reagents: Chemists Develop Environmentally Friendly Method for Synthesising Aniline Derivatives
An international team of researchers, including chemists from HSE University and the A.N. Nesmeyanov Institute of Organoelement Compounds of the Russian Academy of Sciences (INEOS RAS), has developed a new method for synthesising aniline derivatives—compounds widely used in the production of medicines, dyes, and electronic materials. Instead of relying on toxic and expensive reagents, they proposed using tetrahydrofuran, which can be derived from renewable raw materials. The reaction was carried out in the presence of readily available cobalt salts and syngas. This approach reduces hazardous waste and simplifies the production process, making it more environmentally friendly. The study has been published in ChemSusChem.
How Colour Affects Pricing: Why Art Collectors Pay More for Blue
Economists from HSE University, St Petersburg State University, and the University of Florida have found which colours in abstract paintings increase their market value. An analysis of thousands of canvases sold at auctions revealed that buyers place a higher value on blue and favour bright, saturated palettes, while showing less appreciation for traditional colour schemes. The article has been published in Information Systems Frontiers.